Category: Income Tax
Order in absence of DIN non-est as per CBDT Circular 19 of 2019
Please find attached an update on the recent ruling of Delhi High Court wherein it is held that any communication including communication of assessment order not bearing a Document Identification Number (“DIN”) is non-est in law.
Delhi High Court ( in the case of CIT vs Brandix Mauritius Holdings Ltd ITA No 163/2023) upholds quashing of assessment order passed by the Delhi Bench of ITAT where AO has not quoted DIN in the assessment order. The High Court holds that CBDT Circular No 19/2019 dated 14th August, 2019 to the effect that ‘any communication without DIN shall be treated as invalid and shall be deemed to never have been issued is binding on the Revenue. The High Court further holds such omission of quoting DIN in the body of the communication will not be saved by Section 292B of the Act. Dismisses appeal filed by Revenue against the order of ITAT. Oral Order dictated in open court.
INCOME TAX ON CELL TOWER RENT WHICH IS ILLEGAL UNDER BYE LAW 169
No TDS on interest income up to Rs 50,000 in case of senior citizens
No TDS on interest income up to Rs 50,000 in case of senior citizens, clarifies CBDT
CBDT has clarified that in the case of senior citizens, no TDS is required to be deducted u/s 194A, where the amount of such income doesn’t exceed Rs 50,000 in aggregate.

It may be noted that earlier a deduction of Rs 10,000 in respect of interest income was provided to all taxpayers.
Are you a senior citizen and your bank is still deducting TDS on your interest income which is less than Rs 50,000 in a financial year? Here’s good news for you. The Central Board of Direct Taxes has clarified that in the case of senior citizens, no TDS (tax deducted at source) is required to be ‘deducted at source’ u/s 194A of the Income Tax Act, where the amount of such income during a financial year doesn’t exceed Rs 50,000 in aggregate.
In a circular, CBDT has said that it has been brought to its notice that in case of senior citizens, some TDS deductors and banks are deducting TDS despite the amount of income not exceeding Rs 50,000 in a financial year. “The same is not in accordance with the law as the Income-Tax Act provides that no tax deduction at source under section 194A shall be made in the case of Senior Citizens where the amount of such income or, the aggregate of the amounts of such income credited or paid during the financial year does not exceed Rs 50,000,” it said.
The Tax Department further said that under sub-rule (5) of Rule 31A of the I-T Rules, 1962, the Director General of Income-tax (Systems) is authorized to specify the procedures, formats and standards for the purposes of furnishing and verification of the statements or claim for refund in Form 26B and shall be responsible for the day-to-day administration in relation to furnishing and verification of the statements or claim for refund in Form 26B in the manner so specified.
“In exercise of the powers delegated by the CBDT(Board) under sub-rule (5) of Rule 31A of the I-T Rules, 1962, the Principal Director General of Income-tax (Systems) hereby clarifies that no tax deduction at source under section 194A shall be made in the case of Senior Citizens where the amount of such income or, the aggregate of the amounts of such income credited or paid during the financial year does not exceed Rs 50,000.”
It may be noted that earlier a deduction of Rs 10,000 in respect of interest income was provided to all taxpayers. However, to provide a dignified life to senior citizens, significant incentives were given to them in the Budget 2018-19 by FM Arun Jaitley. One such incentive was given in the form of exemption of interest income on deposits with banks and post offices up to Rs 50,000 without TDS under Section 194A. For this purpose, a new Section 80TTB was inserted in the I-T Act to provide deduction for interest income up to Rs 50,000. This benefit is also available on interest income from all FDs and recurring deposit schemes.
Compliance Handbook 2018-19 – Vinay Jagetiya
Includes
- Income Tax
- GST
- Companies Act
- LLP
- Useful Websites
- Compliance Calendar
Very Useful
Click Here to download
Income Tax return required for Road Accidental Death Compensation
Accidental Death & Compensation:
(Income Tax Return Required)
If a person has an accidental death and the person was filing income tax returns for the last three years, then the government is obliged to give ten times the average annual income of the last three years to that person’s family.
Yes, you will be surprised by this, but this is right and it is Government rule. For example, if someone’s annual income is 4 lakh 5 lakhs and 6 lakhs in the first, second and third years respectively, its average income is ten times of five lakhs.. means five million rupees, family of that person is entitled to receive from the Government.
In the absence of much information, people do not take this claim with the Government.
If any return is missing, mainly last three years, this could lower the claim amount or even no claim because court takes ITR as only evidence. NO wealth record, FD’s; business etc. is given that much importance as compared to ITR in the eyes of law.
Many a time, people do not file ITRs regularly..or it will be taken lightly..
Due to lack of information the family receives no economic benefits.
Source – forwarded
Section 166 of the Motor act, 1988 (Supreme Court Judgment under Civil/ Appeal No. 9858 of 2013, arising out of SLP (c) No. 1056 of 2008) Dt. 31 Oct. licvaithi
Accidental Death & Compensation:
(Income Tax Return Required)
What is the last date of filing Income Tax Returns 2018?
 Income Tax Returns Filing: As the date nears, here are the guidelines on how to file your tax returns (physical or online) easily.
Income Tax Returns Filing: As the date nears, here are the guidelines on how to file your tax returns (physical or online) easily.
The last date for filing the annual income tax return (ITR) for the financial year 2018-19 or assessment year 2018-19 to the Income Tax Department is July 31.
It is mandatory for people to file tax returns if their gross total income (before allowing deductions under section 80C to 80U) exceeds Rs 250,000 in a financial year. The limit is Rs 300,000 for senior citizens (more than 60 years old, but less than 80 years old) and Rs 500,000 for super-senior citizens (more than 80 years old).
One can file his/her return involuntarily even if your income is less than the maximum exemption limit. As the date nears, here are the guidelines on how to file your tax returns (physical or online) easily:
Also Read | How to file Income Tax Returns Form-1 (Sahaj) online
Offline method:
When filing the ITR Form-1 (Sahaj) form offline, you will need to take a print and fill it up in order to submit it. Once the tax department receives your form, it will send you an acknowledgment.
However, not everybody is allowed to fill the form offline. Those who can do so are:
– Super senior citizens (80 years and above)
– Individuals or HUF whose returns are without refund claims in the IT returns
– Those whose income is of up to Rs5 lakh
Online method:
There are two ways of filling the form online. One is by manually entering all details and submitting the return online. The other is by uploading XML files through offline methods.
Submitting online:
This form needs to be submitted to the Income Tax Department’s website.
Log on to http://www.incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in. You will need to keep your user ID, password and date of birth ready for this. You will also be asked to enter a captcha code.
When you sign in, click on the option which says “Filling of Income Tax Return”
Select the ITR form name, choose the assessment year as well as the submission mode. You will need to prepare this and submit it on the website itself.
Also Read | Income tax e-filing: These 5 websites can help you file your ITR
Fill in the rest of the details as required and hit the submit button.
The system will generate a message of acknowledgement which will tell you that your income tax return has been submitted successfully. After this, the ITR-V would pop up on the screen. This will be the acknowledgement and you will need to download this. The ITR-V would also be sent to the email id you have registered with the IT Department website.
Uploading XMLs:
Log on to the website http://www.incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in. Go to the homepage. Click on the “Offline Utilities” option.
You will come across another option which says “Income Tax Return Preparation Utilities”.
Choose the Assessment Year for which you are filling the income tax return.
Download the offline utility (Excel or Java)
Prepare the income tax return form offline at your convenience, save it and extract XML files.
Then go online again, click on the “Filing of Income Tax Return” option and submit the XML files.
E-verify your the filing of your return within 120 days of submitting it to complete the process.
Also Read | Income tax e-filing: How to file different categories of ITR forms online
Documents needed to file ITR
For filing income tax returns (offline or online), you need to keep handy checklist of several details including bank account details, PAN number, pay slips, rent receipts for claiming HRA, address of the house property.
New Income-tax Return Forms for non-profits – Huge data mining exercise on part of the Government of India
The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) has notified the Income-tax Return (ITR) Forms applicable for the Assessment Year 2018-19. These ITR Forms will be applicable for filing income-tax return in respect of income earned during the period 1st April 2017 to 31st March 2018. The new forms incorporate the changes made by the Finance Act, 2017 in the Income-tax Act, 1961. It is apparent that the new ITR Forms have shifted the entire onus on the taxpayers to prove their claim for deductions, expenses or exemptions.
Form ITR 7 (Applicable to trusts and charitable institutions)
Trusts and institutions established for charitable purpose are required to file their annual income-tax Return in ITR 7. Aadhar number of trust functionaries like trustees must be disclosed as also amount of foreign contributions received and for what purpose. In our view, there is a huge data-mining exercise on part of the Government of India.
It is mandatory for a trust or charitable institution to file return of income electronically with or without digital signature. A trust may also file return of income under Electronic Verification Code. However, a trust liable to get its accounts audited under section 44AB shall furnish the return electronically under digital signature.
Trusts & charitable institutions to disclose more information in ITR 7
Charitable or religious trusts filing income-tax return for the Assessment Year 2018-19 (Financial Year 2017-18) in Form ITR 7 shall be required to disclose following additional information:
- Aggregate annual receipts of the projects/institutions run by the trust. However, the table asking details about the name and annual receipts of institutes covered under Sections 10(23C)(iiiab), (iiiac), (iiiad) and (iiiae) has been removed.
- Date of registration or approval granted to the trust.
- Amount utilized during the year for the stated objects out of surplus sum accumulated during an earlier year.
Details of fresh registration upon change of objects (Section 12A)
Section 12A provides for conditions to be satisfied by a charitable institution for availing of exemption under sections 11 and 12. A new clause (ab) has been inserted in Section 12A(1) with effect from Assessment Year 2018-19 to provide that where a charitable institution has been granted registration and, subsequently, it has adopted or undertaken modification of the objects which do not conform to the conditions of registration, it shall be required to take fresh registration. Consequential changes have been made in the Form ITR 7. A trust will be required to furnish the following details if there is any change in its stated objects:
- Date of change in objects
- Whether application for fresh registration has been made within stipulated time period?
- Whether fresh registration has been granted?
- Date of such fresh registration.
No deduction for corpus donations made to other institutions (Section 11)
Up to Assessment Year 2017-18, a donation made by a registered trust to another registered trust constituted application of income notwithstanding that the donation was made with a specific direction that it shall form part of the corpus of the donee. The Finance Act, 2017 has inserted a new Explanation 2 with effect from Assessment Year 2018-19 to effect that any donation to another charitable institution registered under section 12AA with a specific direction that it shall form part of the corpus of the donee, shall not be treated as application of income for charitable or religious purposes.
The consequential changes have been made in form ITR 7. In Schedule TI (Statement of Income) all the corpus donations made by a trust to another registered trust shall be added back to the taxable income of the donor trust.
Due date & penalty
A trust which is required to get its accounts audited under the Income-tax Act or under any other law, the due date is September 30 of the relevant assessment year.
Finance Act, 2017 has levied new fees if an Assessee does not furnish the return of income on the due dates prescribed under Section 139(1). The amount of such late filing fees shall be: INR 5,000 if return is furnished after the due date, but, before December 31 of the assessment year (INR 1,000 if total income is up to INR 5 lakhs) and INR 10,000, in any other case.
After introducing this new provision, the Assessee shall now be required to pay the late filing fees under section 234F along with interest under section 234A, 234B and 234C before filing of return of income. The Income-tax department shall not be required to initiate the penalty proceedings separately to levy such fees on late filers. Relevant changes have been incorporated in the new ITR forms wherein a new row is added to enable the Assessee to fill the details of late filing fees.
View latest ITR 7 at:
https://www.incometaxindia.gov.in/forms/income-tax%20rules/2018/itr7_english.pdf
https://capnewsviews.blogspot.in/2018/04/new-income-tax-return-forms-huge-data.html?m=1
FIXED INCOME Investor Interest 5% TDS if Rent over Rs50,000pm
How to Link Pan Number with Aadhar Card
How to Link Pan Number with Aadhar Card
Both the PAN card as well as the Aadhar card are unique identification cards that serve as proof of identity that are necessary for registration and verification purposes. The Process to link your Aadhar number with PAN numner or Income Tax Return has been announced by Income Tax Department on July 13, 2015.
Income Tax Department(ITR) has given the facility to link Permanent Account Number (PAN) with the unique identification Number or Aadhar number. It helps you to eliminate the process of sending ITR – V to CPC(Centralised Processing Centre) in Bangalore.
Although PAN Card will be linked with Aadhar number only , if your personal details like Name, Gender, Date of Birth matches with Aadhar data as per PAN Data.
Income Tax Department will validate your name, date of birth, gender as per PAN and Aadhar Number with Centralized database of Unique Identification Authority of India(UIDAI). Please note that if the details do not match, the Aadhar number will not be linked to your PAN.
After the completion of Aadhar and PAN number linking process, you can e-verify your return if your mobile number is registered with UIDAI.
Please be noted that once you linked your Pan number with Aadhar card, you cann’t delinked it. As of now Income Tax Department has not given the facility to delinking PAN number with Aadhar. Follow the simple guide to link PAN number or Income Tax Return with Aadhar number(UID):
- Login to income tax e-Filing portal.

- When you logged into the e-filling portal, a pop up window appears on your screen to link your Aadhar Number.
- If the pop up window will not show automatically, you can go to profile settings under the main menu and click on the link that says Aadhar linked to PAN.
- Before entering the Aadhar card , be sure to verify your Name, Gender, Date of Birth should matches with PAN Card details.
- Income tax department will validate all your details and then after cross verifying all the details, enter your Aadhar number, text code.
Note: Don’t have Aadhar Card. Check guide on How to get Aadhar Card.
- At last, Click on Link Now.
- After validation, Aadhar number will be linked to your PAN number.
Note: Aadhar will be linked only if the details match.
How to generate EVC through Income Tax site?
- Login to income tax e-Filing portal.
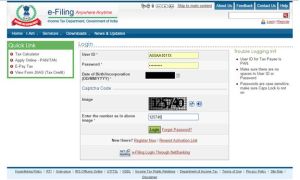
Note: There are two ways to generate EVC(Electronic verification Code). One is via your Netbanking account or second is via your registered email address/phone number. These steps works for second method.
- Enter the EVC received on your registered email address/mobile number.
- Click on e-verify return under the E-file tab.

- There will be four options. Choose first option: “I already have an EVC and I would like to Submit EVC”. Provide the EVC in the text box. Click Submit.
- Download the Acknowledgement document. Your e-filing is complete. No further action is required from your end now.
Note: In future, Aadhar card not only will be useful but also mandatory to avail benefits of various government schemes and services. I recommend you to check numerous other benefits of having Aadhar Card.
Contributed by Anuradha Chawla – AadharCard.in




